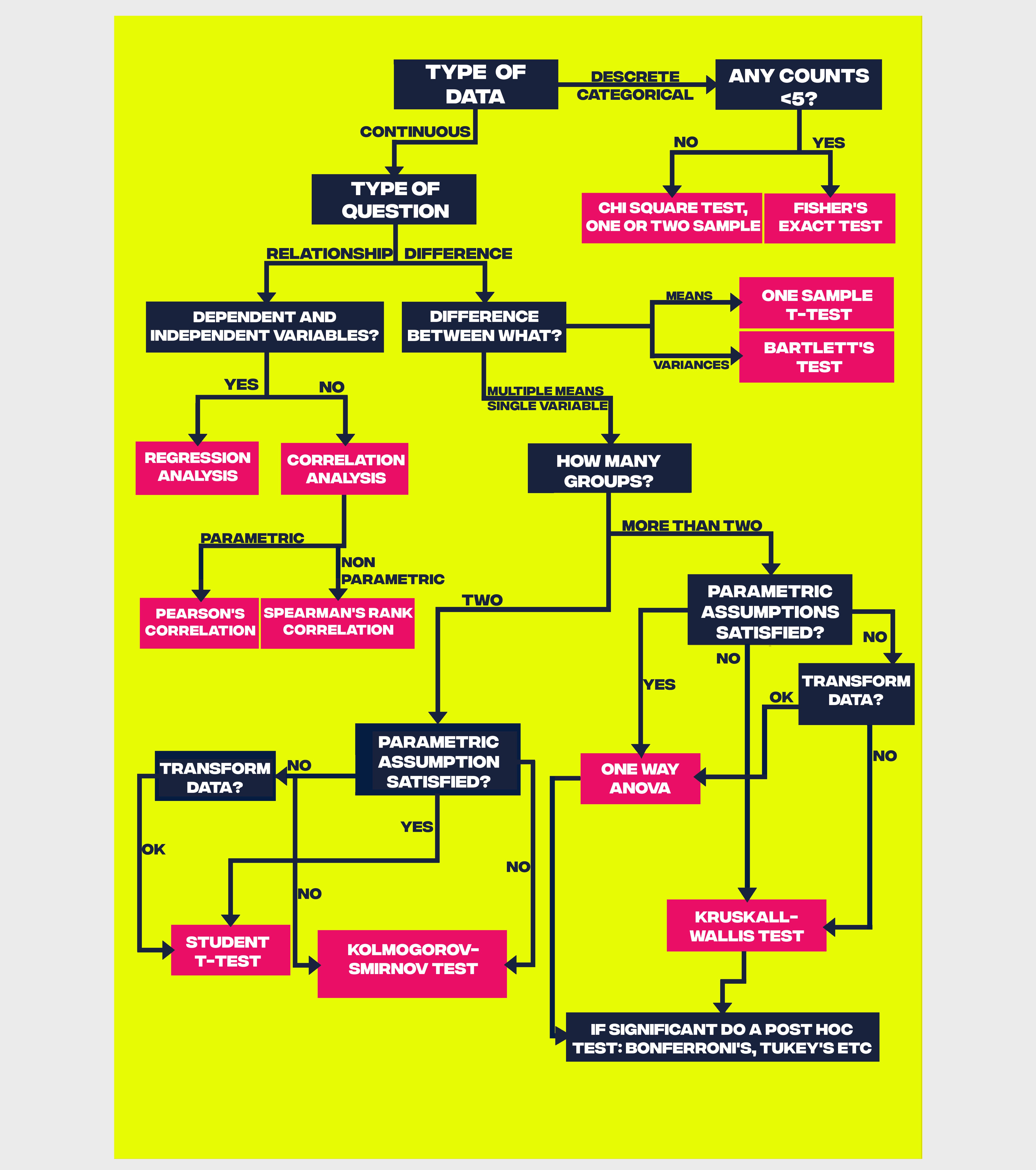
The field of statistical analysis is very vast and the number of different models and tests you may want to build/apply on your data may look overwhelming. It is important that you always start from the analysis of the structure of your data to identify what could be a good/bad analysis (e.g. you may need to use a non-parametric test if your data are not normally distributed).
Equally important is to always start from a clear and defined research question, just randomly try to apply different tests/models will make it very difficult for you to assess the results and it will compromise your analyis. One of the easeast misstep you can occur onto is confusing correlation with causation. The only way to assess proper causation is knowing your sample and established clear hypothesis to test.
Below there is a list of principles you may want to get accustomed with: